LTC4225-1/LTC4225-2
18
422512f
applicaTions inForMaTion
Power Prioritizer
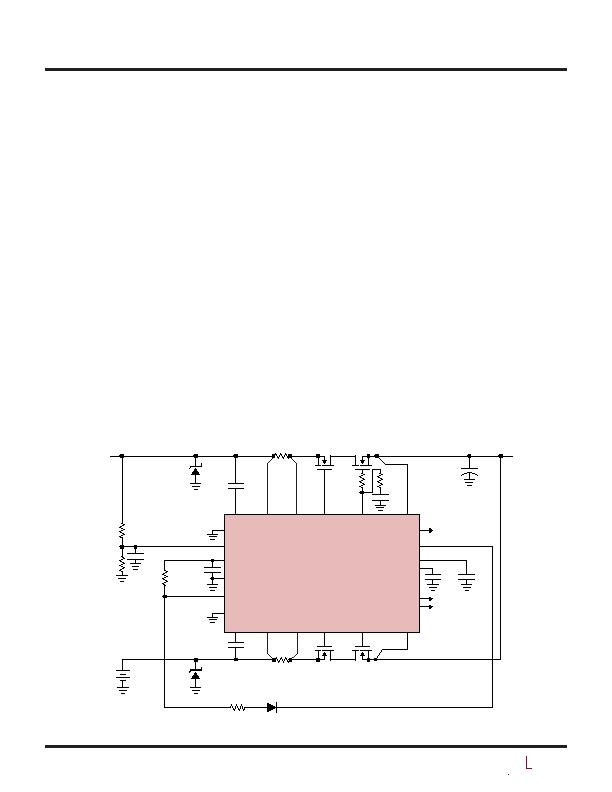
Figure 8 shows an application where either of two supplies
is passed to the output on the basis of priority, rather than
simply allowing the highest voltage to prevail. The 5V pri-
mary supply (INPUT 1) is passed to the output whenever
it is available; power is drawn from the 12V backup supply
(INPUT 2) only when the primary supply is unavailable. As
long as INPUT 1 is above the 4.3V UV threshold set by the
R1-R2 divider at the ON1 pin, M
H1
is turned on connecting
INPUT 1 to the output. When M
H1
is on, PWRGD1 goes
low, which in turn pulls ON2 low and disables the IN2
path by turning M
H2
off. If the primary supply fails and
INPUT? drops below 4.3V , ON1 turns off M
H1
and PWRGD1
goes high, allowing ON2 to turn on M
H2
and connect the
INPUT 2 to the output. Diode D1 ensures that ON2 remains
above 0.6V while in the off state so that when ON2 goes
high, M
H2
is turned on immediately without invoking the
100ms turn-on delay. When INPUT 1 returns to a viable
voltage, M
H1
turns on and M
H2
turns off. The ideal diode
MOSFETs M
D1
and M
D2
prevent backfeeding of one input
to the other under any condition.
Additional Applications
In most applications, the back-to-back MOSFETs are con-
fgured with the MOSFET on the supply side as the ideal
diode and the MOSFET on the load side as the Hot Swap
control. But for some applications, the arrangement of the
MOSFETs for the ideal diode and the Hot Swap control may
reversed as shown in Figure 9. The Hot Swap MOSFET is
placed on the supply side and the ideal diode MOSFET on
the load side with the source terminals connected together.
If this configuration is operated with 12V supplies, the
gate-to-source breakdown voltage of the MOSFETs can
be exceeded when the input or output is connected to
ground as the LTC4225s internal 12V clamps only limit
the DGATE-to-IN and HGATE-to-OUT pin voltages. Choose
a MOSFET whose gate-to-source breakdown voltage is
rated for 25V or more as 24V voltage can appear across
the GATE and SOURCE pins of the MOSFET during an
input or output short. As shown in Figure 9, if a MOSFET
with a lower rated gate-to-source breakdown voltage is
chosen, an external Zener diode clamp is required between
the GATE and SOURCE pins of the MOSFET to prevent it
from breaking down.
Figure 8. 2-Channel Power Prioritizer
CPO1
ON1
EN1
ON2
EN2
INTV
CC
GND
C
CP1
0.1礔
C1
0.1礔
C
F1
0.1礔
C
HG1
33nF
C
L
470礔
C
T2
47nF
Z1
SMAJ13A
INPUT 1
INPUT 2
5V
PRIMARY
SUPPLY
12V
BACKUP
SUPPLY
C
CP2
0.1礔
C
T1
47nF
IN1
SENSE1 DGATE1
M
D1
SiR466DP
M
H1
SiR466DP
LTC4225
R
S1
0.006
M
D2
SiR466DP
M
H2
SiR466DP
R
S2
0.006
R3
3.92k
D1
LS4148
HGATE1
R
H1
10
R
HG1
47
V
OUT
5A
OUT1
CPO2
IN2
SENSE2 DGATE2
HGATE2
OUT2
422512 F08
FAULT1
PWRGD2
FAULT2
Z2
SMAJ13A
R4
41.2k
R2
49.9k
R1
20k
PWRGD1
TMR1
TMR2
+
+
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。
相关PDF资料
LTC4230CGN#TRPBF
IC CONTRLLR HOT SWAP TRPL 20SSOP
LTC4232CDHC#TRPBF
IC CTLR HOT SWAP 5A 16-DFN
LTC4240IGN#TRPBF
IC CTRLR HOTSWAP CPCI I2C 28SSOP
LTC4241IGN#PBF
IC CTRLR HOTSWAP 3.3V AUX 20SSOP
LTC4242CUHF#TRPBF
IC CNTRLR HOT SWAP 38-QFN
LTC4244CGN-1#TRPBF
IC CTRLR HOTSWAP PCI 20-SSOP
LTC4245CG#TRPBF
IC CNTRLR HOT SWAP 36-SSOP
LTC4251-2CS6#TRPBF
IC CTRLR HOTSWAP NEGVOLT SOT23-6
相关代理商/技术参数
LTC4225IGN-1#TRPBF
功能描述:IC CTLR HOT SWAP DUAL 24-SSOP RoHS:是 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> PMIC - 热交换 系列:- 产品培训模块:Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS
Obsolescence Mitigation Program 标准包装:119 系列:- 类型:热交换控制器 应用:通用型,PCI Express? 内部开关:无 电流限制:- 电源电压:3.3V,12V 工作温度:-40°C ~ 85°C 安装类型:表面贴装 封装/外壳:80-TQFP 供应商设备封装:80-TQFP(12x12) 包装:托盘 产品目录页面:1423 (CN2011-ZH PDF)
LTC4225IGN-2#PBF
功能描述:IC CONTROLLER HOT SWAP 24-SSOP RoHS:是 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> PMIC - 热交换 系列:- 产品培训模块:Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS
Obsolescence Mitigation Program 标准包装:119 系列:- 类型:热交换控制器 应用:通用型,PCI Express? 内部开关:无 电流限制:- 电源电压:3.3V,12V 工作温度:-40°C ~ 85°C 安装类型:表面贴装 封装/外壳:80-TQFP 供应商设备封装:80-TQFP(12x12) 包装:托盘 产品目录页面:1423 (CN2011-ZH PDF)
LTC4225IGN-2#TRPBF
功能描述:IC CTLR HOT SWAP DUAL 24-SSOP RoHS:是 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> PMIC - 热交换 系列:- 产品培训模块:Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS
Obsolescence Mitigation Program 标准包装:119 系列:- 类型:热交换控制器 应用:通用型,PCI Express? 内部开关:无 电流限制:- 电源电压:3.3V,12V 工作温度:-40°C ~ 85°C 安装类型:表面贴装 封装/外壳:80-TQFP 供应商设备封装:80-TQFP(12x12) 包装:托盘 产品目录页面:1423 (CN2011-ZH PDF)
LTC4225IUFD-1#PBF
功能描述:IC CONTROLLER HOT SWAP 24-QFN RoHS:是 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> PMIC - 热交换 系列:- 标准包装:50 系列:- 类型:热交换控制器 应用:-48V 远程电力系统,AdvancedTCA ? 系统,高可用性 内部开关:无 电流限制:可调 电源电压:11.5 V ~ 14.5 V 工作温度:-40°C ~ 85°C 安装类型:表面贴装 封装/外壳:10-TFSOP,10-MSOP(0.118",3.00mm 宽) 供应商设备封装:10-MSOP 包装:管件
LTC4225IUFD-1#TRPBF
功能描述:IC CTLR HOT SWAP DUAL 24-QFN RoHS:是 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> PMIC - 热交换 系列:- 产品培训模块:Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS
Obsolescence Mitigation Program 标准包装:119 系列:- 类型:热交换控制器 应用:通用型,PCI Express? 内部开关:无 电流限制:- 电源电压:3.3V,12V 工作温度:-40°C ~ 85°C 安装类型:表面贴装 封装/外壳:80-TQFP 供应商设备封装:80-TQFP(12x12) 包装:托盘 产品目录页面:1423 (CN2011-ZH PDF)
LTC4225IUFD-2#PBF
功能描述:IC CONTROLLER HOT SWAP 24-QFN RoHS:是 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> PMIC - 热交换 系列:- 产品培训模块:Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS
Obsolescence Mitigation Program 标准包装:119 系列:- 类型:热交换控制器 应用:通用型,PCI Express? 内部开关:无 电流限制:- 电源电压:3.3V,12V 工作温度:-40°C ~ 85°C 安装类型:表面贴装 封装/外壳:80-TQFP 供应商设备封装:80-TQFP(12x12) 包装:托盘 产品目录页面:1423 (CN2011-ZH PDF)
LTC4225IUFD-2#TRPBF
功能描述:IC CTLR HOT SWAP DUAL 24-QFN RoHS:是 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> PMIC - 热交换 系列:- 产品培训模块:Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS
Obsolescence Mitigation Program 标准包装:119 系列:- 类型:热交换控制器 应用:通用型,PCI Express? 内部开关:无 电流限制:- 电源电压:3.3V,12V 工作温度:-40°C ~ 85°C 安装类型:表面贴装 封装/外壳:80-TQFP 供应商设备封装:80-TQFP(12x12) 包装:托盘 产品目录页面:1423 (CN2011-ZH PDF)
LTC4226
制造商:LINER 制造商全称:Linear Technology 功能描述:Wide Operating Range Dual Hot Swap Controller Fast Response Limits Peak Fault Current
